Every time Google crawls your site, it uses a Googlebot. Googlebot is a web crawler that fetches pages and adds or updates them in the Google index. Unfortunately, fake Googlebots exist that spoof real Googlebots, often for malicious activity such as DDoS attacks. In fact, the number of fake Googlebots is actually increasing.
So how can we tell the real Googlebots from the fake ones?
This post looks at how Log Hero simplifies and automates this process and provides a step-by-step guide on detecting fake Googlebots.
What Are Fake Googlebots?
A Googlebot (like any web crawler) identifies itself through its user agent string. A user agent string is part of a server log file used to identify who is accessing your website. A user agent string can look like this:
“Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; Googlebot/2.1; +http://www.google.com/bot.html)”
Fake Googlebots manipulate this user agent string to appear to the server like a genuine Googlebot–fake Googlebots will often have the exact same user agent string as a genuine Googlebot.
This means that when it comes to log file analysis, just looking at the user agent string alone is not enough to tell whether your site is being visited by a fake Googlebot or not.
How Much Traffic Is From Fake Googlebots?
A recent Incapsala report that looked at billions of search engine visits to websites from search engines estimated that around 4% of all Googlebots are fake, i.e. they are not who they claim to be. Depending on the website, the purpose of the faked Googlebot, and the level of security, this number can be as high as 25%.
Why Do People Use Fake Googlebots?
By faking Googlebots hackers can gain access to secure parts of a website. DDoS attacks are one of the most common malicious uses of fake Googlebots. A Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack is an attempt to make an online service unavailable by overwhelming it with traffic from multiple sources.
Other uses of fake Googlebots include stealing content, spamming, and other hacking attacks and security breaches.
Fake Googlebots not only present a security threat, they also make your analytics data inaccurate. As an SEO, you need to be able to rely on your data in order to correctly optimize your site.
There are some positive reasons for spoofing Googlebots but they are beyond the scope of this article.
What Are the Best Ways to Detect Fake Googlebots?
The method recommended by Google is to perform a reverse DNS lookup. Basically, by checking the IP address that is accessing your site, you can confirm whether this is actually from Google or not. (Check out this article to see a step-by-step reverse DNS lookup.) However, performing this process on each user agent string in your data can be extremely time-consuming.
Detect Fake Googlebots Automatically with Log Hero
Log Hero has developed an innovative solution to this problem: server log file data is piped straight into Google analytics and clever custom dimensions can be used to filter this data.
To detect fake Googlebots, we recommend creating a custom report with all the custom dimensions related to detecting bots.
You can do this from the Customization tab in your Log Hero Google Analytics property:
Customization > Custom Reports > New Custom Report
Give your report a name and select the Flat Table view.
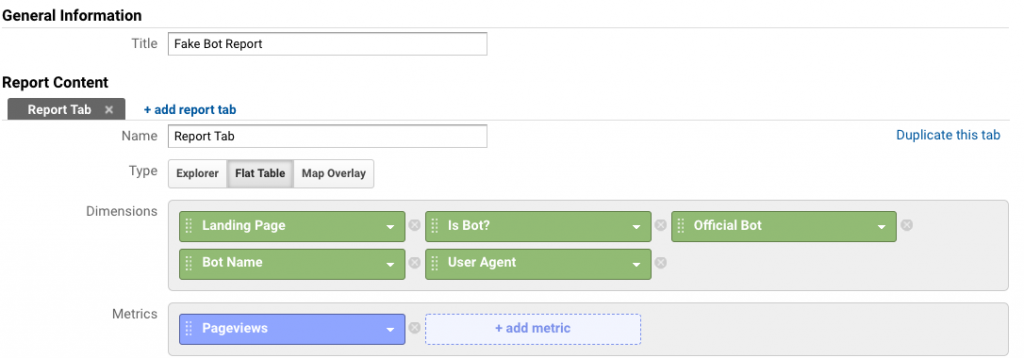
In a custom report, you can add up to five secondary dimensions (including custom dimensions) and even more metrics.
We recommend starting with the dimension you would like to order your data by. In this example, we have chosen to order the data by landing page.
Next, we add the Log Hero custom dimensions:
- Is Bot– Is Bot is a binary true/false answer to whether the session was triggered by a bot. If true, it was a bot, if false, it was a human.
- Official Bot– This is a binary true/false answer that tells you if the bot is genuine of fake. If true, the bot is an official Googlebot.
- Bot Name–This variable tells you which search engine bot accessed your site.
- User Agent– This dimension returns the user agent string.
Finally, we need to add a metric. We have chosen to sort by pageviews – this corresponds to the number of times a particular bot visits each landing page.
Now, click Save and you will be able to see the data in your new custom report.
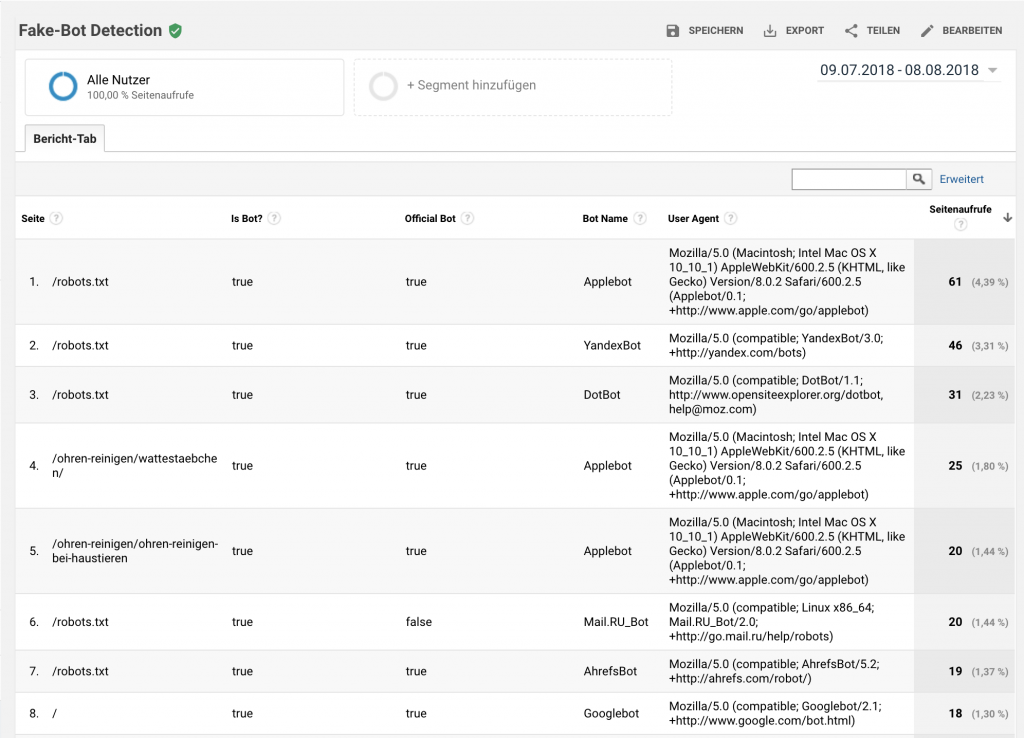
Interpreting the Data
Let’s interpret this data. To find the fake bots check the Official Bot column. In the sixth row in the example above, we can see this value is returned as false. This means we have identified a fake bot. Looking at the next column we can see that it is a fake Mail.Ru bot. Finally, we can see the user agent and the number of times this bot crawled the /robots.txt page.
Now you have this custom report set up, it makes detecting fake Googlebots (and other fake bots) easy.
Upgrade to a Paid Plan for More Custom Dimensions
Note: the custom dimensions Bot Name, and Official Bot are only available to Log Hero customers with paid plans. For free Log Hero users, only the user agent string data is available. But in order to verify the genuine Googlebot traffic, you need to export this data and perform a reverse DNS lookup on each user agent string. This method is pretty tedious.
Why not upgrade to a paid plan to enjoy more custom dimensions and automatically detect fake Googlebots?
New to Log Hero? Get started today with a free plan, or check out some more of our resources.
